What is phishing?
In today's digital world, where email, social media, and messaging platforms are part of everyday life, phishing has become one of the most common threats to businesses and individuals. However, in recent years, this type of attack has alarmingly evolved with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), becoming more sophisticated, harder to detect, and dangerous for companies of all sizes.
This type of attack, based on social engineering techniques, aims to deceive users into gaining access to confidential information such as passwords, banking data, or corporate system credentials.
How does a traditional phishing attack work?
An attacker impersonates a trusted entity —such as a bank, a digital platform, or even a colleague— in order to manipulate the victim into taking some dangerous action:
- Click on fake links.
- Download infected files.
- Entering your credentials on fraudulent websites.
- Provide personal or sensitive information through messages or calls.
These attacks often arrive disguised as urgent communications, verification requests, or false security warnings.
Traditional types of phishing
There are different traditional forms of phishing, and knowing them is key to preventing incidents:
Email phishing: It is the most common type. It involves sending fake emails that pretend to be legitimate and contain malicious files or links.
Spear phishing: Targeted attacks with personalized information.
Smishing: Attack via SMS, with messages that contain malicious links.
Vishing: This type of attack involves making phone calls to obtain data through voice.
Pharming: It is carried out by performing a hidden redirection to fake websites through DNS manipulation.
Signs to recognize a traditional phishing attempt
There are certain signs that can help you identify an attack before falling into the trap:
- Alarmist messages that demand immediate action.
- Grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, or inconsistencies in the message.
- Links that do not match the official domain.
- Emails from senders that do not match the official domain, or with addresses similar to the real ones
- False data or information, or that does not correspond to the general message of the email.
Analysis of a real phishing case
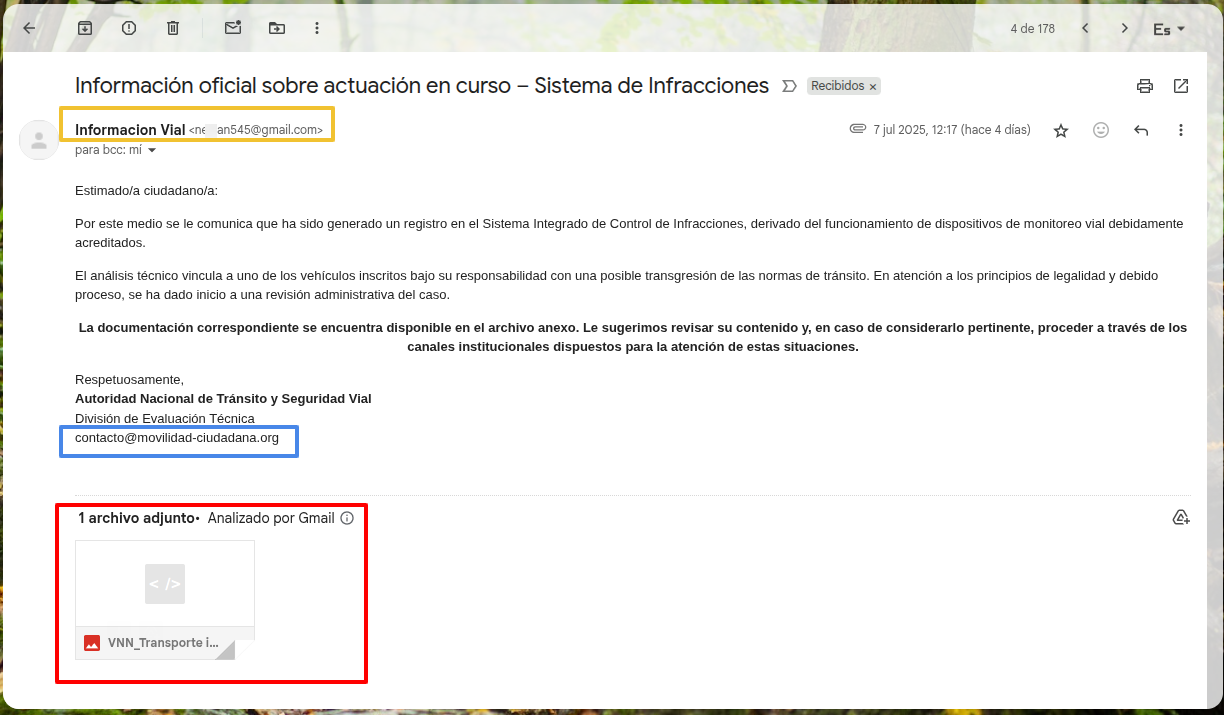
Screenshot of a real phishing email message.
In the previous image, we can see a real example of a phishing attack; let's analyze its content to identify malicious signals:
- Alarmist messages that demand immediate action: The message talks about a violation and an ongoing action, and urges the user to take a dangerous action (download and open the attachment). We have the first warning sign.
- Grammatical, spelling, or inconsistencies in the message: No obvious spelling or punctuation errors are observed. The message is clear, concise, and well-written (possibly with the help of AI). Nevertheless, we can identify two inconsistencies in the message:
- The domain associated with the email of the signature does not exist (in the blue box of the image: movilidad-ciudadana.org), it is a domain that is not registered, therefore that email account does not exist either. We have a second warning sign.
- In the malicious message, the entity sending the information is the "Integrated System for Violation Control," which for the victim, located in Medellín, Colombia, would correspond to the "Mobility Secretariat," which is affiliated with the municipality of Medellín, and whose website is https://www.medellin.gov.co/es/secretaria-de-movilidad/. This incongruity in the name of the entity throughout the message is our third warning sign.
- Links that do not match the official domain: This message does not contain external links; instead, it contains an attachment (in the red box of the image), which may contain malicious code. Do not click on the links or download attachments until you are sure the message is legitimate. If the message has external links, hover over the link without clicking, so you can see the URL to which the link redirects; they should be links to the official site of the entity sending the message, in this example the links should redirect to the site https://www.medellin.gov.co.
- Emails from senders that do not match the official domain, or with addresses similar to the real ones: In this example, we can see that the sender of the message (the yellow box in the image) is a Gmail account of a regular user, when it should be an email under the domain medellin.gov.co (for example noreply@medellin.gov.co), as it is supposed to be the entity that sends us the message. We have our fourth warning signal.
- False data or information that does not correspond to the general message of the email: In this example, we clearly identify that the email contacto@movilidad-ciudadana.org does not exist as of the date of writing this article, and also that the name of the entity sending the message does not correspond with the name of the actual entity in the geographical location where the victim resides.
With all the warning signs we were able to identify in the previous example, we can conclude that this is a phishing attack, more specifically of the email phishing type.
New threats enhanced by AI
Generative artificial intelligence has taken phishing to another level, equipping cybercriminals with tools that allow them to execute much more precise and sophisticated attacks.
1. Automated emails with AI
The attackers use models like ChatGPT to:
- Write messages without errors, convincing, and tailored to the recipient's tone.
- Generate automatic responses in real time.
- Create large-scale multilingual campaigns.
2. Vishing with voice cloning
With just seconds of audio, they can replicate a manager's voice and make calls that seem legitimate:
Real example: Someone used AI to impersonate Secretary of State Marco Rubio and contact chancellors.
3. Deepfakes in video calls
They impersonate a real person in a video to request access or transfers with apparent legitimacy.
4. Phishing chatbots
Fake websites integrate AI virtual assistants to simulate technical support or identity verification, guiding victims step by step.
5. Fake profiles on social media
Realistic identities are created with AI-generated photos to scam through chat, fake work relationships, or make false offers.
Why is AI phishing more dangerous?
AI models allow for the development of more sophisticated and elaborate attacks, targeting more precise objectives, executing them quickly and on a large scale, and with a high level of credibility.
- Automatic personalization Greater credibility and effectiveness.
- Multichannel (text, voice, image) Simultaneous attacks from different fronts.
- Speed and scale Thousands of messages in minutes.
- Zero errors Hard to distinguish the false from the real.
Measures to protect your business from phishing
At SmartBox Host, we recommend implementing a proactive and educational approach:
- Always verify the sender: especially in urgent messages.
- Inspect the links before clicking: hover over them and check the URL.
- Cross-checking: When faced with a suspicious instruction, confirm through another direct means before taking action.
- Clear and well-known policies: Define formal procedures for password changes, remote access, transfers, etc., and train your team on these.
- Organizational culture: It promotes training, critical thinking, and the adoption of internal policies.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable it on all possible access points, mandatory for critical access
- Never share credentials: Avoid sharing access via email, message, or call.
- Continuous training: Update your team on new threats, not just the classic ones.
- Behavioral Analysis (UEBA): Use tools that detect anomalous actions.
- Control of internal AI use: Limit and monitor its use in sensitive processes.
- Advanced filters: Use anti-phishing tools and endpoint protection.
Analysis from social engineering
Social engineering is based on deceiving a person into voluntarily revealing sensitive information or performing a dangerous action. Phishing is one of its most common forms, and it relies more on human factors than technical ones.
Key strategies to prevent phishing from social engineering
1. Awareness and continuous training
The user is the primary target, and they can also be the first line of defense.
- Implement awareness campaigns about phishing and manipulation.
- Conduct internal phishing simulations for training without consequences.
- Teach to identify signals: urgency, emotional pressure, subtle errors, suspicious links.
A trained user does not click reflexively, but thinks before acting.
2. Foster critical thinking
Helps users question the context before trusting.
- Why are you asking me for this information?
- Is this email or message consistent with what I normally receive?
- Is emotional pressure being used to force me to act quickly?
When something seems strange or too urgent, it's better to verify before acting.
3. Foster a culture of "it's okay to doubt"
Many employees do not report suspicious things for fear of making a mistake or looking foolish. It should be:
- Create safe channels to report suspicions (without retaliation).
- Validate and reward proactive behavior.
- Remember that no system is infallible, which is why human oversight is essential.
4. Reduce exposure to social vectors
Limit the amount of information made public to the minimum required:
- Do not share institutional emails on public sites or open directories.
- Restrict the posting of internal information on social media (for example, hierarchies, job titles, personnel changes).
- Limit the amount of visible data in email signatures (avoid direct phone numbers, personal IDs).
The attackers use this information to make their messages more credible (spear phishing).
5. Clear policies known to everyone
Establish policies, communicate them to the work group, and promote their practical adoption. For example:
- Establish that no one from the IT, finance, or human resources team will ask for passwords or codes via email or phone call.
- Define formal procedures for password changes, remote access, transfers, etc.
- Communicate those policies to the entire organization and ensure that they are followed.
If employees know what should never be requested via email, phone, or other digital means, they will more easily identify fraudulent attempts.
6. Verbal or visual authentication in critical situations
When an unusual request is received through a digital channel, it should be confirmed by a reliable secondary source:
- Direct call.
- Internal video call.
- Message through official channels such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, or verified internal services.
- Personally.
Example from social engineering
A person receives an email from the "Chief Financial Officer" urgently requesting a transfer. The attacker clones their signature and copies their writing style.
Prevention through social engineering:
- The employee is trained to identify urgent emails as potential threats.
- There is a policy that requires dual validation for transfers.
- Call the official CFO number directly and confirm that it is fake.
Result: attempt blocked thanks to human training and protocol, not just a technical filter.
Preparation is the best defense
Phishing is not an issue exclusive to end users. Companies are also frequent targets of these attacks, and a single wrong click can compromise the security of your entire digital infrastructure.
At SmartBox Host, we help you protect your work environment through cybersecurity solutions, threat detection, and ongoing education for your team.
Do you want to strengthen the security of your company?
Contact us today and schedule a free evaluation.
Phishing 2.0: How cybercriminals use artificial intelligence to trick your company.